Is ₹2 Crore FD Interest Enough for a Monthly Income? Explained

Fixed Deposits (FDs) are a popular investment choice for individuals seeking a stable and secure source of income. Many investors wonder whether a ₹2 crore FD interest per month is sufficient to sustain their lifestyle. The answer depends on various factors such as FD interest rates, inflation, and individual expenses. In this article, we will analyze the potential monthly income from a ₹2 crore FD and whether it is enough to meet financial needs.
Understanding FD Interest Rates
FD interest rates vary across banks and financial institutions. They depend on the tenure of the deposit, the type of investor (senior citizens often get higher rates), and the prevailing economic conditions. Typically, interest rates range from 6% to 8% per annum in India. Higher rates offer better returns, making it crucial to choose the best FD scheme for maximizing earnings.
Additionally, different types of FDs offer different interest structures. Some FDs provide cumulative interest, which is paid at the end of the tenure, while others offer non-cumulative interest, paying out monthly, quarterly, or annually. Investors seeking a monthly income must opt for non-cumulative FDs to receive regular payouts.
Calculating Monthly Interest on a ₹2 Crore FD
The formula to calculate interest earnings on an FD is:
Simple Interest:
Compound Interest (Quarterly Compounded):
Where:
- P = Principal amount (₹2 crore)
- r = Annual interest rate
- n = Number of times interest is compounded per year (quarterly = 4)
- t = Tenure in years
Expected Monthly Interest Payouts
Below is an approximate breakdown of monthly interest based on different FD interest rates:
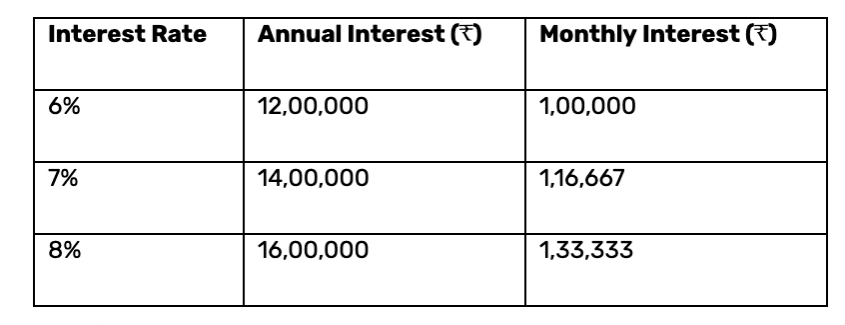
From this table, we can see that with an FD interest rate of 7%, a ₹2 crore FD can generate ₹1.16 lakh per month, which might be sufficient for some individuals but not for those with higher expenses.
Factors Affecting the Sufficiency of FD Interest Income
1. Inflation
The cost of living increases over time, reducing the purchasing power of money. If inflation rises at 5% per annum, the real value of interest income declines, making it challenging to maintain the same lifestyle.
2. Lifestyle and Expenses
A monthly income of ₹1-1.3 lakh might be sufficient for a frugal lifestyle but may not cover luxury expenses, medical emergencies, or inflation-adjusted living costs. Expenses such as rent, groceries, healthcare, education, and travel should be taken into account.
3. Tax Implications
FD interest is fully taxable under the Income Tax Act, 1961. If the investor falls into the highest tax bracket (30%), a significant portion of the income will go towards taxes, reducing net earnings. For example, if an individual earns ₹1.16 lakh per month from FD interest and is taxed at 30%, their post-tax income reduces to approximately ₹81,667 per month.
4. Alternative Investment Options
Instead of relying solely on FDs, diversifying investments into mutual funds, real estate, and dividend-yielding stocks can provide a more stable and inflation-adjusted income. Other options such as Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS), Post Office Monthly Income Scheme (POMIS), and debt mutual funds can offer competitive returns.
5. Emergency Fund Consideration
Since FD interest rates fluctuate based on economic policies, it is crucial to maintain an emergency fund. Medical expenses, unforeseen financial crises, or rising living costs can put stress on fixed-income investments like Fixed Deposit. Having a diversified backup fund ensures financial security.
6. Interest Rate Variability
Banks revise FD interest rates based on economic conditions, making long-term financial planning challenging. Investors should compare rates from different banks and opt for the best available schemes with high stability.
Strategies to Optimize FD Returns
1. Laddering FDs
Laddering involves investing in multiple FDs with varying maturity periods instead of locking the entire amount into a single long-term FD. This strategy helps in mitigating interest rate fluctuations and provides liquidity at different intervals.
2. Opting for Tax-Saving FDs
Tax-saving FDs offer deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, up to ₹1.5 lakh per annum. While these FDs have a lock-in period of 5 years, they provide tax benefits that can help in overall wealth preservation.
3. Choosing Senior Citizen FDs
Senior citizens enjoy higher FD interest rates, usually 0.5% higher than regular FDs. Those above 60 years should leverage these schemes for better returns.
4. Diversifying Investments
Investors should not rely entirely on FDs. Allocating funds into Government Bonds, Corporate Deposits, REITs, and dividend-yielding equities can provide higher post-tax returns and better hedge against inflation.
5. Using Monthly Payout FDs
Banks offer monthly income FDs that provide regular interest payouts. These schemes ensure liquidity while maintaining capital security.
Conclusion
A ₹2 crore FD interest per month can provide a stable income, but its sufficiency depends on various factors like FD interest rates, inflation, taxation, and personal expenses. At an average interest rate of 7% per annum, it generates around ₹1.16 lakh per month, which may be enough for a moderate lifestyle but not for individuals with higher financial needs. However, after accounting for taxes and inflation, the real value of this income diminishes over time.
To ensure long-term financial security, investors should consider a diversified portfolio instead of relying solely on FDs. Investing in a combination of Fixed deposit, debt funds, equity funds, and real estate can provide better inflation-adjusted returns. Additionally, financial planning should include emergency funds, medical insurance, and alternative income sources to achieve financial stability. Understanding these aspects will help make better financial decisions for sustained wealth growth.